The elements of art are the fundamental components used by artists when creating a work of art. These elements, often referred to as the building blocks of art, include line, shape, value, colour, space, texture, and form. Artists use all of these elements together help create the composition of an artwork, to express meaning and to create the impression of a scene or subject.
In this guide, discover what the elements of art are and how you can use them to create successful compositions.
Disclaimer: Fine Art Tutorials is a reader supported site. When you make purchases through links on this site, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.

Line

Line is one of the most basic elements of art and it can be used to create many different effects. Lines can be straight, curved, angular or organic and they may be thick or thin. They can also denote direction, such as horizontal or diagonal. Lines can also be used to suggest movement, value, depth and texture within a piece of art.

An artwork can be created with just line alone, look at line art drawings, where artists use pens or pencils alongside the hatching or cross hatching techniques to create the impression of light and shadow in different subjects.
Shape

Shapes are two-dimensional forms that are defined by an outline or border. They can be geometric such as squares, circles and triangles, or organic like free-form shapes. Artists use shapes to represent a subject, for example, drawing the shape of a leaf in a landscape piece.

Complex shapes draw more attention from the viewer than simple shapes and large shapes draw more attention than smaller shapes, due to the inherent visual weight these types of characteristics have. William Morris repeated shapes and design motifs in his designs to create his famous patterns. The shapes all appear complex, organic and representational.
Value

Value is the lightness or darkness of a colour used in an artwork. Light and dark values create depth and perspective and also emphasise certain elements within a composition. Value is created by mixing black or white with a colour.
Denman Ross created the value scale in 1907. In the Denman Ross value scale, 1 represents white and 9 represents black. Using a value scale can help artists determine relative values in their reference, which can aid them in mixing. For example, it can tell artists how much black or white to mix into their colours to match it to the colours in their reference.
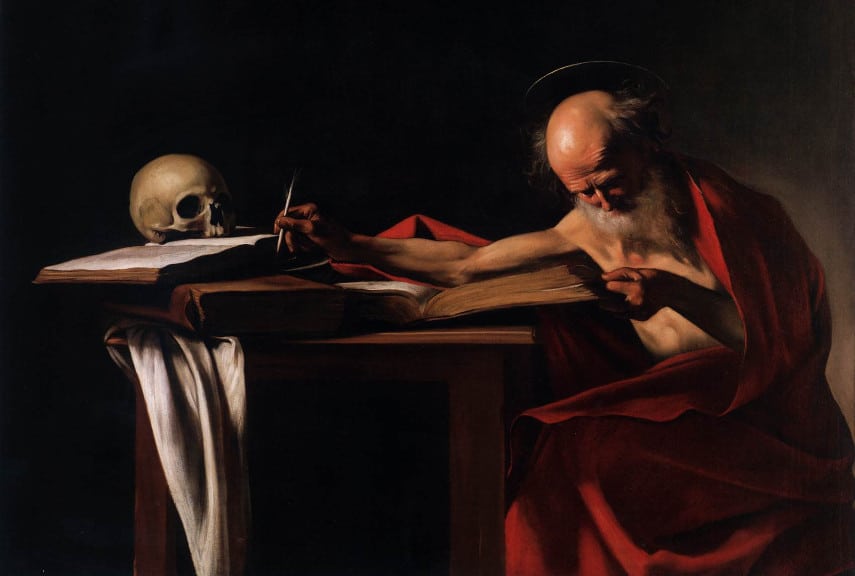

Chiaroscuro is the technique of using highly contrasting light and dark values in an artwork. Oil painters such as Caravaggio and Rembrandt used this technique in their oil paintings to create drama, atmosphere and focal points.
Colour

Colour is an important element of art which helps to bring life to an artwork. Colour is the way in which humans perceive wavelengths of light and is further categorised by hue, saturation and luminance.
Primary colours such as red, blue and can be mixed to create secondary and tertiary colours. In art, these primary and secondary colours correspond to particular pigments which can be mixed to create new tones and hues.
Colours evoke different feelings in people and they can be used to help express an artist’s emotional state. Colour theory is the study of the applications of colour in art and is an important concept to understand when creating artworks, as it can help artists to become faster and more accurate at colour mixing and help artists create colour harmony with intent in their designs.

Artists may also choose to use a colour scheme in their artwork to bring unity to a painting. Monet used colour schemes extensively in his paintings. The split complementary scheme in the ‘Banks of the Seine at Jenfosse’ creates variety, whilst unifying different sections of the painting.
Space

Space is the area around, within and between shapes that creates a sense of depth within an artwork. Positive space is defined as the space in artworks occupied by subject or objects, while negative space is the area around and between the subjects. Negative space could include the background, or sky for instance, however this can depend on the context of the artwork. You can see how Escher uses positive and negative space cleverly in his artwork ‘Metamorphosis II’. The repeated elements of the insects on the left morph into appearing as negative space between the fish in the middle, then transform into bird shapes on the right hand side of the artwork. Escher played with using similar shapes and consistent values to create a transformation of occupied space in this artwork.

Depending on how the artist has chosen to position and space elements within an artwork, feelings of harmony, unity and tension can be created. When subjects and objects are placed within close proximity of one another, it can create a sense of tension but also a sense of unity. However, when subjects and objects are more evenly space, the composition will appear more balanced.
Texture
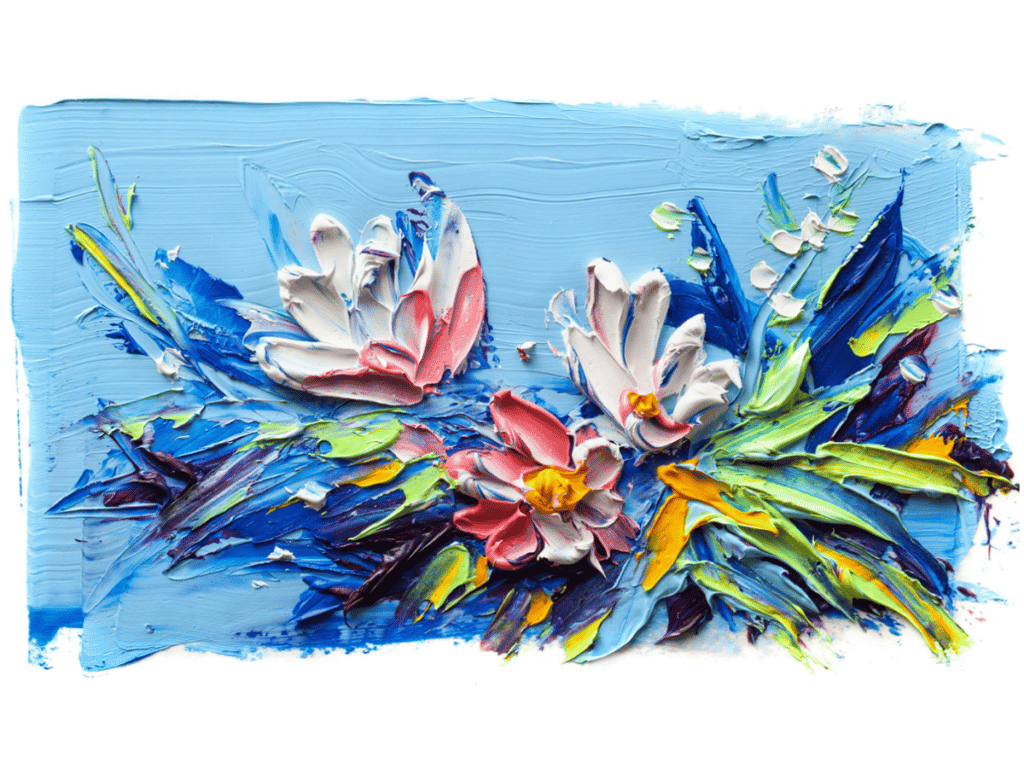

Texture refers to the surface quality of an object or material that can be seen and felt. It can make a painting look more three-dimensional or realistic and it also helps to create a sense of depth, movement and rhythm.
Sculptures have inherent texture to them, with paint, artists can add additives to paint to enhance texture. For example, by adding cold wax to oil paint, it will thicken the mixture and make the paint retain brushstrokes on the canvas.
Form
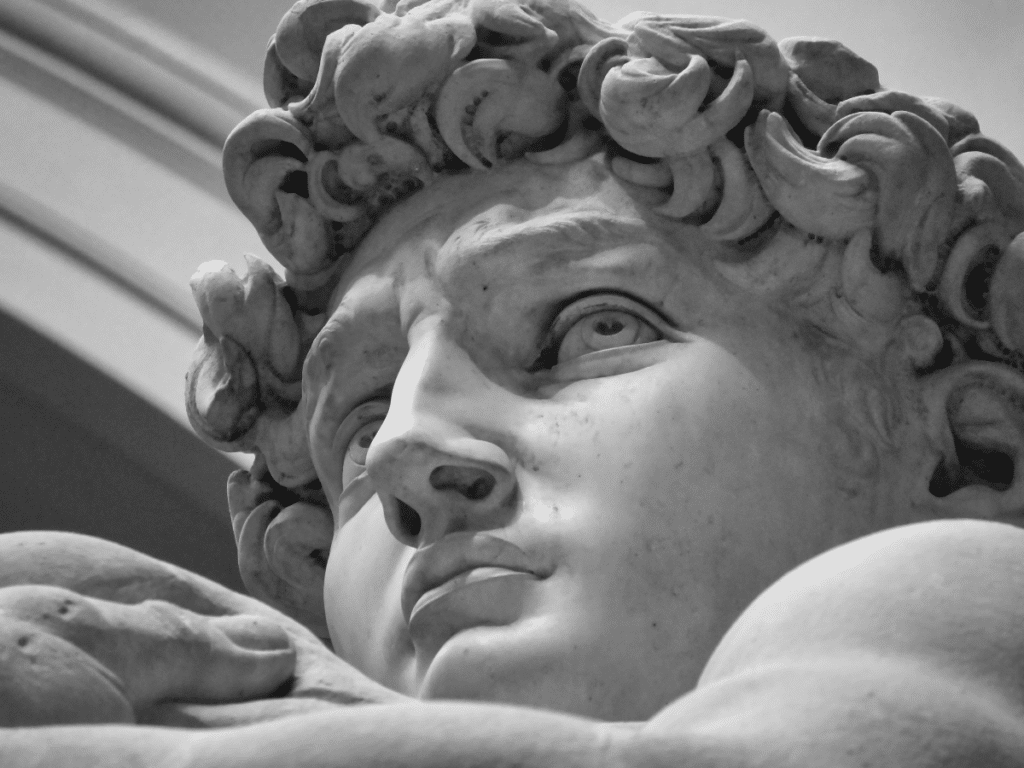
Form is a three-dimensional object that has mass and volume. It occupies space and it can be viewed from any angle. Sculptures are considered to have three dimensional form, while subjects within a painting can have the appearance of form. Forms can be organic or geometric, simple or complex and either abstract or representational. When using media to create two dimensional artworks, such as pencil or paint, artists can create the impression of form by using shape, colour and values to give the illusion of three dimensionality.
Examples: Elements of art

Vincent van Gogh used the elements of art in interesting and unique ways to create novel, symbolic and eye catching compositions. For example, he used the complementary colour scheme of purple and yellow in his famous painting ‘The Starry Night’ to create contrast and dynamism. Additionally, the use of repeated, textured brush strokes creates a sense of movement and rhythm. The brushstrokes appear as lines moving and swirling in the sky, which adds to the sense of atmosphere in the piece.

Gustav Klimt use different elements to create harmony and variety in his artworks. For example, in his painting ‘The Kiss’, he repeats geometric, simple shapes across the clothing of the figures, creating subtle contrast and variety by introducing blocks of colour. The repeated elements unify the design and create rhythm.
Principles of design
The principles of design are the effects that can be created by arranging visual elements in such a way to create a successful composition. These include balance, contrast, emphasis, repetition, variety, proportion, scale, movement, pattern, rhythm and unity.
Balance can be achieved through a symmetrical or an asymmetrical composition; artists use this by arranging their elements in such a way that it feels harmonious and unified. For example, the artist could repeat a similar shape on one side of the canvas to match a shape on the other. This symmetry offers balance to the composition.
Artists can create the effect of contrast by using elements that are dissimilar to one another together. For example, colours on opposite ends of the colour wheel contrast with each other, because they are dissimilar in hue. By placing orange next to blue, the two colours contrast against and therefore emphasise each other.
Formal analysis
Formal analysis is the process of looking at and examining the elements, principles and techniques used in an artwork. By observing an artwork and breaking it down into its component parts, one can gain deeper understanding of how the elements interact with each other to create a unique composition. Viewers can also elicit important information about the context of the artwork, such as the style of the artist, the date it may have been created and the meaning behind the work. This can help to identify which techniques were used to create the artwork and why.

For instance, Impressionist artists such as Monet used looser shapes to represent subjects, compared to Renaissance artists, with more textured brush strokes and more vivid colours. This is a style that was common during the 19th century. By doing a formal analysis of a painting like this, the viewer could glean information such as the century that the painting might have been from and the intent behind representing the subject in this manner.
Visual weight of elements
The visual weight of an element is determined by its size, shape, colour and value. Larger shapes or darker colours tend to have more visual weight than smaller shapes or lighter colours. This is because they appear to be more dominant on the canvas and draw the eye’s attention more.

For example, in a portrait piece, the artist might use dark tones to emphasise certain features of the subject’s face. This would draw viewer’s attention to these points on the canvas and create focus.
The importance of the elements of art
The elements of art are the building blocks of any artwork. By understanding and using each element effectively, an artist can create compositions that have clarity and purpose. Study how to use them in combination with one another, to create visual effects such as balance or contrast. The visual weight of elements is also important in creating focus and emphasis on particular points of the composition.
Formal analysis is a great tool for understanding the elements of art and how they interact together in a piece. Viewers can understand the style and context of artwork by looking at how the visual elements created it.
Overall, the elements of art are important components in creating a successful artwork. Knowing how to use them effectively will help any artist in creating compositions that have impact and meaning.

